Jobseeker’s Allowance (JSA) is a financial support benefit designed to help people who are actively looking for work.
But a common question many job seekers have is: is Jobseeker’s Allowance means tested? The answer depends on the type of JSA you are talking about.
While income-based JSA was means-tested, New Style JSA is not generally means-tested, although some exceptions apply.
What Is Jobseeker’s Allowance and Who Can Claim It?

Jobseeker’s Allowance is a financial benefit designed to provide temporary support for people who are unemployed or working less than 16 hours a week. It is aimed at those actively seeking work and willing to follow specific job search requirements.
Historically, there were two main types of JSA:
- Income-based JSA – a means-tested benefit where eligibility depended on the claimant’s household income and savings.
- Contribution-based JSA (now known as New Style JSA) – based on an individual’s National Insurance contributions in recent years.
Eligibility for JSA generally requires that the claimant:
- Is aged 18 or over (some exceptions apply for 16- and 17-year-olds in certain circumstances)
- Is under State Pension age
- Lives in England, Scotland or Wales
- Is unemployed or working fewer than 16 hours per week
- Is actively seeking employment and willing to attend Jobcentre Plus appointments
How Does Income-Based Jobseeker’s Allowance Work?
Income-based JSA was designed for individuals who had not made enough National Insurance contributions but still required financial help while searching for work. This type of benefit was means-tested, meaning the Department for Work and Pensions (DWP) considered:
- Your income from all sources
- Your savings and investments
- Your partner’s income and savings, if applicable
If savings exceeded £16,000, claimants would usually not be eligible. Savings above £6,000 would reduce the amount paid.
Earnings from part-time work could also reduce the benefit amount depending on the income level.
Although income-based JSA is still received by some existing claimants, new applications are no longer accepted.
Those who would have qualified are now directed towards Universal Credit, which combines several benefits into one monthly payment.
What Is New Style Jobseeker’s Allowance and How Is It Different?

New Style Jobseeker’s Allowance (JSA) is the current version of contribution-based JSA, offering short-term financial support to individuals actively seeking work.
Unlike income-based JSA, which was means-tested, New Style JSA focuses on a person’s work history and National Insurance contributions rather than their current income or savings.
How New Style JSA Is Funded and Determined?
New Style JSA is funded through the National Insurance system. To qualify, claimants must have paid, or been credited with, sufficient Class 1 National Insurance contributions in the two full tax years before the year of the claim.
These contributions are typically made when working as an employee, although certain benefits like Statutory Sick Pay can provide credited contributions.
This requirement ensures that New Style JSA acts as an insurance-based benefit rather than a needs-based one.
Why New Style JSA Is Not Generally Means-Tested?
Unlike income-based JSA, New Style JSA does not usually take into account:
- Your personal savings or investments
- Your partner’s income or savings
- Most forms of unearned income
This makes it particularly useful for people who have recently lost a job but may have savings or a partner in employment. It provides a safety net without penalising individuals for having financial reserves.
Exceptions Where Income Can Affect Payments
While New Style JSA is not generally means-tested, there are situations where income can impact the amount received:
- Pension income: If you receive a pension of more than £50 per week, the amount over £50 will be deducted from your JSA. For example, if your pension is £70, your JSA would be reduced by £20.
- Part-time earnings: If you work fewer than 16 hours a week, your earnings may still reduce your JSA if they exceed a certain threshold. The Department for Work and Pensions calculates this reduction on a case-by-case basis.
Duration and Payment Schedule
New Style JSA is typically available for up to 182 days, which is roughly six months. Payments are made every two weeks directly into the claimant’s bank account.
After this period, if the claimant still requires financial help, they may need to apply for Universal Credit or other forms of support.
Key Differences Between New Style JSA and Income-Based JSA
| Feature | New Style JSA | Income-Based JSA |
| Based on National Insurance contributions | Yes | No |
| Means-tested | No (with limited exceptions) | Yes |
| Partner’s income affects claim | No | Yes |
| Time-limited | Yes (182 days) | No fixed limit |
| Still available for new claims | Yes | No (replaced by Universal Credit) |
These distinctions highlight that New Style JSA operates more like an insurance policy you have paid into during your working life, while income-based JSA was a means-tested welfare benefit.
How Do You Apply for Jobseeker’s Allowance in the UK?
The process for claiming JSA is straightforward but requires meeting specific steps. For New Style JSA, the application is completed online through the official government website. The steps include:
- Completing the online application form and submitting details of work history, personal information, and National Insurance number.
- Providing proof of identity, which may include a passport or driving licence.
- Attending an initial interview at the local Jobcentre Plus to agree on a work search commitment.
The work search commitment is a personalised agreement outlining the actions a claimant will take to find work. It can include applying for a set number of jobs each week, attending training sessions, or improving CVs.
Missing appointments or failing to meet the agreed job search activities can result in sanctions, which reduce or stop payments for a set period.
How Are Jobseeker’s Allowance Payments Calculated?
The amount of JSA a person can receive depends on their age, work status, and any deductions from part-time earnings or pensions. For New Style JSA in 2025, the standard weekly rates are:
| Age Group | Weekly Rate | Notes |
| Under 25 | £67.20 | Can be reduced by part-time earnings or pension income |
| 25 and over | £84.80 | Same deductions apply |
Part-time earnings are treated in a specific way. A set amount can be earned before deductions begin, after which every pound over that limit reduces the JSA payment.
Pension income over £50 per week reduces JSA payments pound for pound above that threshold. For example, if a claimant has a pension of £60 per week, their JSA would be reduced by £10.
How Does JSA Compare to Universal Credit?
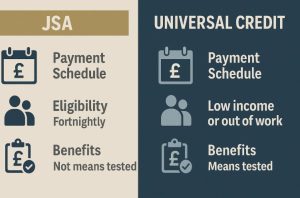
Universal Credit has largely replaced income-based JSA and provides a more comprehensive system for those with low income. The key differences include:
| Feature | New Style JSA | Universal Credit |
| Means-tested | No (with exceptions for pensions and part-time earnings) | Yes |
| Based on National Insurance contributions | Yes | No |
| Payment frequency | Fortnightly | Monthly |
| Can include housing and family support | No | Yes |
For those who have a strong National Insurance record and do not require housing or childcare support, New Style JSA may be sufficient.
However, individuals with low income and little savings may receive more overall support through Universal Credit.
What Are the Current Work Search and Reporting Requirements for JSA?
To remain eligible for Jobseeker’s Allowance, claimants must meet strict work search and reporting requirements set by the Department for Work and Pensions (DWP).
These rules ensure that JSA is only paid to individuals who are actively seeking employment and making reasonable efforts to secure work.
The Work Search Commitment
At the start of a claim, every applicant will agree to a work search commitment during an interview at Jobcentre Plus. This personalised document outlines the actions a claimant must take each week to improve their chances of finding work. It can include:
- Applying for a specific number of jobs per week
- Updating or creating a CV and cover letter
- Registering with recruitment agencies
- Searching online job boards daily
- Attending training or skills development programmes
This commitment is tailored to the claimant’s skills, experience, and the local job market. Failure to follow it can lead to sanctions.
Regular Jobcentre Plus Appointments
Claimants are usually required to attend Jobcentre Plus every two weeks. During these meetings, they will:
- Discuss their job search activities
- Provide evidence of applications and interviews
- Receive job leads or referrals to training courses
- Review and update their work search commitment if necessary
Missing these appointments without a valid reason can result in payments being stopped temporarily or permanently.
Evidence of Job Searching
The DWP requires claimants to keep a detailed record of their job search activities, which can be reviewed at any time. Acceptable evidence includes:
- Copies of job applications or confirmation emails
- Notes from phone calls with employers
- Screenshots of online job searches
- Interview invitations or rejection letters
Keeping thorough and organised records helps avoid disputes about whether the claimant is meeting their obligations.
Sanctions and Their Impact
If a claimant does not meet their work search or reporting requirements, they may face sanctions. Sanctions can be:
- Low level: for missing appointments or being late without a good reason
- Medium level: for failing to take reasonable steps to find work
- High level: for refusing a suitable job offer or leaving a job voluntarily without good cause
The length of a sanction depends on the severity and whether it is a first, second, or third offence. In some cases, sanctions can last up to 182 days, significantly impacting financial stability.
Flexibility for Special Circumstances
The DWP can adjust work search requirements in special cases, such as:
- Health issues or disabilities that limit the type of work a person can do
- Caring responsibilities that affect availability for work
- Temporary life events such as bereavement or moving house
These adjustments must be discussed with a Jobcentre Plus adviser and recorded in the work search commitment.
What Common Misunderstandings Exist About JSA and Means-Testing?

Many people are unaware of the differences between the old income-based JSA and the current New Style JSA. Common misconceptions include:
- Believing all JSA is means-tested, when in fact New Style JSA is not affected by savings or most types of income.
- Assuming that everyone who is unemployed automatically qualifies, when eligibility depends on National Insurance contributions.
- Thinking that JSA is a long-term benefit, when it is actually designed for short-term support during the job search process.
These misunderstandings can lead to confusion and, in some cases, prevent eligible people from applying for the benefit they are entitled to.
Conclusion
Jobseeker’s Allowance is not entirely means-tested. The older income-based JSA was means-tested and has mostly been replaced by Universal Credit.
New Style JSA, which is currently available, is contribution-based and not generally affected by income or savings, although pensions and part-time work can reduce the amount received.
If you are unemployed or working part-time, it is worth checking whether you qualify for New Style JSA or whether Universal Credit might be more suitable for your situation.
FAQs
Is New Style JSA affected by my partner’s income?
No, your partner’s income or savings do not usually affect New Style JSA.
How many hours can I work while receiving JSA?
You can work up to 16 hours per week, but earnings above a certain threshold can reduce your payments.
Can I claim JSA if I have a pension?
Yes, but pension income over £50 per week will be deducted from your JSA.
What happens if I fail to meet my work search requirements?
You may face sanctions, which can reduce or stop your payments for a period of time.
Is JSA backdated if my claim is approved late?
It can be backdated in certain circumstances, but you must provide a valid reason for the delay.
Can I get both JSA and Universal Credit?
You can claim New Style JSA alongside Universal Credit if you meet the eligibility criteria for both.
What happens when my JSA entitlement ends?
You may need to apply for Universal Credit or other benefits if you still require financial support.






